Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a widespread but serious condition that can lead to tooth loss if not treated early. It affects the gums and the tissues supporting your teeth, significantly impacting your overall oral health. Here’s what you need to know about it, its signs, causes, and treatments:
Signs and Symptoms:
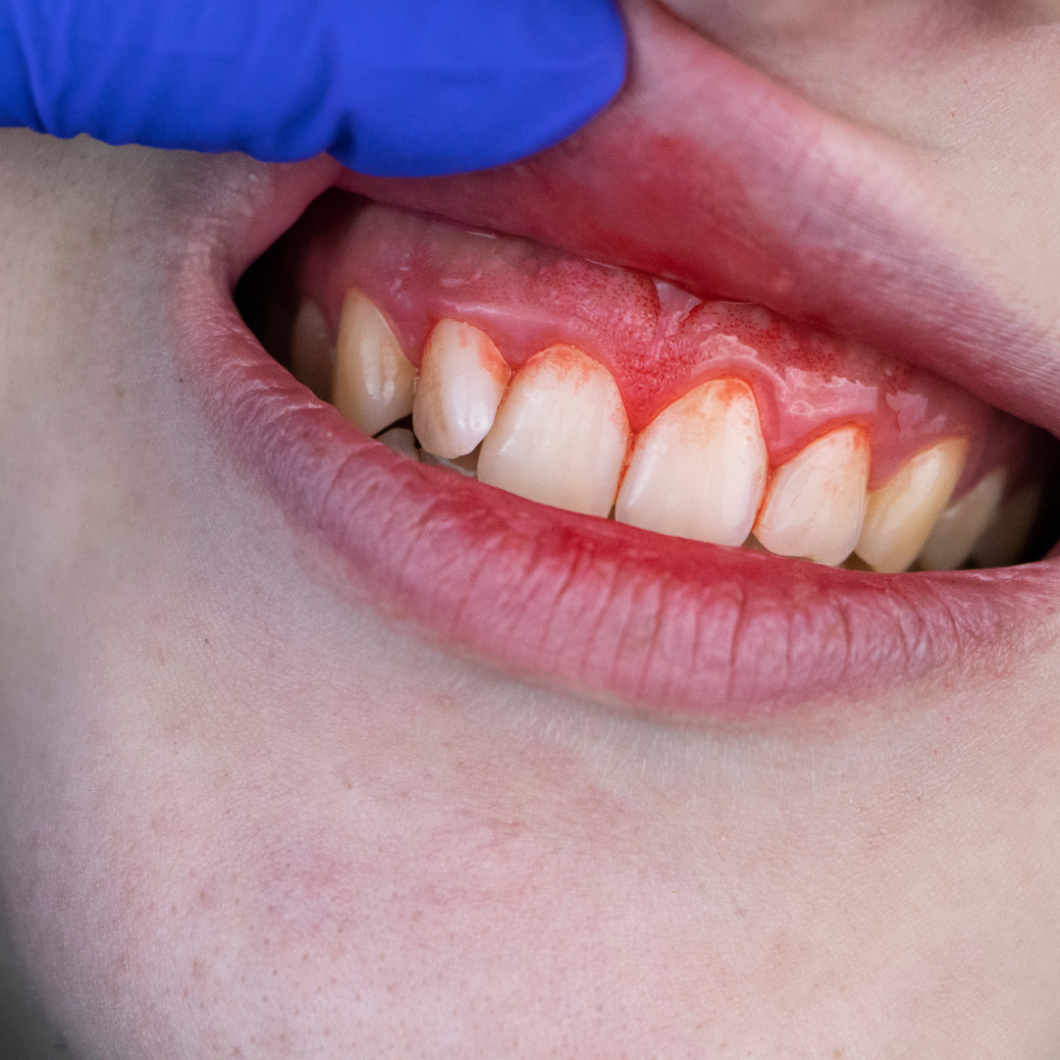
- Red, Swollen, or Tender Gums: Inflammation is one of the first signs of gum disease, causing the gums to become red and tender.
- Bleeding While Brushing or Flossing: Bleeding gums when brushing or flossing often signal gum disease.
- Persistent Bad Breath: Foul-smelling breath, or halitosis, can indicate gum infection and bacterial buildup.
- Receding Gums or Loose Teeth: In more advanced stages, gums may recede, exposing more of the tooth, and teeth may become loose or shift.
Causes of Gum Disease:
Gum disease primarily develops from plaque accumulation, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. When plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which can lead to gum infection. Other factors contributing to it include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing let plaque build up on teeth and gums.
- Smoking or Chewing Tobacco: These habits increase the risk of it and slow healing after treatment.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes and autoimmune diseases can make individuals more vulnerable to gum infections.
Stages of Gum Disease:
- Gingivitis: The earliest stage of gum disease, marked by inflammation. Gingivitis is reversible with proper oral hygiene.
- Periodontitis: In advanced stages, gums pull away from teeth, creating pockets that become infected and may lead to tooth loss if untreated.
Treatment Options:
- Scaling and Root Planing: A deep cleaning that removes plaque and tartar below the gum line to prevent further infection.
- Medications: Dentists may prescribe antibiotics or antimicrobial rinses to fight bacterial infections in the gums.
- Surgical Treatment: In severe cases, surgery such as flap surgery or bone grafts may be required to regenerate lost bone or remove tartar below the gum line.
Conclusion:
Detecting and treating gum disease early is essential to maintaining healthy teeth and gums. Regular dental checkups and good oral hygiene practices at home can help prevent it and keep your smile healthy for years to come.

Leave a Reply